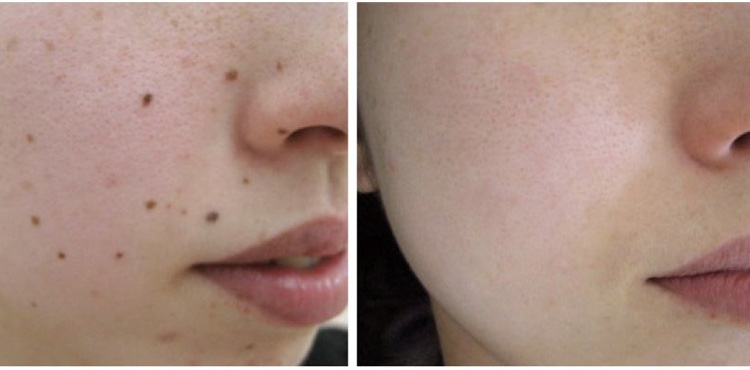
Mole laser surgery, or laser mole removal, is a medical procedure that uses laser technology to remove moles from the skin. Moles are common skin growths composed of pigment cells (melanocytes) and can vary in size, shape, and color. While most moles are harmless, some individuals choose to have them removed for cosmetic reasons or if there is concern about the potential for malignancy.
Here's an overview of the laser mole removal process:
Procedure:
-
Consultation: Before the procedure, you'll typically have a consultation with a dermatologist or healthcare professional. They will examine the mole, assess its characteristics, and discuss the reasons for removal.
-
Preparation: The area around the mole is cleaned, and sometimes a local anesthetic is applied to numb the area.
-
Laser Treatment: A laser device is used to deliver concentrated beams of light onto the mole. The laser energy is absorbed by the pigment cells in the mole, leading to the destruction of the mole tissue.
-
Post-Treatment Care: After the procedure, the treated area may be covered with a dressing, and you'll be provided with care instructions. It's essential to keep the area clean to promote healing and reduce the risk of infection.
Benefits:
-
Precision: Laser mole removal allows for precise targeting of the mole, minimizing damage to surrounding skin.
-
Minimal Scarring: Laser removal may result in less scarring compared to traditional surgical excision methods.
-
No Stitches: Since the procedure is non-invasive, there is typically no need for stitches.
Considerations:
-
Mole Evaluation: Not all moles are suitable for laser removal. The procedure is generally more appropriate for smaller and non-cancerous moles. If there is suspicion of malignancy, a biopsy may be recommended before removal.
-
Multiple Sessions: Depending on the mole's size and characteristics, multiple laser sessions may be necessary for complete removal.
-
Risk of Pigment Changes: There is a risk of temporary or permanent changes in skin pigmentation after laser mole removal. This is more common in individuals with darker skin tones.
-
Potential for Regrowth: In some cases, moles may regrow after laser removal, particularly if the entire pigment cell cluster is not completely destroyed.
Recovery:
Recovery time is generally shorter compared to surgical removal, but there may be some redness, swelling, and crusting in the treated area. It's essential to follow post-procedure care instructions to minimize the risk of complications.
If you're considering laser mole removal, consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional to determine the most suitable method for your specific situation and to ensure proper evaluation of the mole's characteristics. Additionally, regular skin checks and consultation with a healthcare professional are crucial for monitoring any changes in moles and detecting potential skin issues early on.