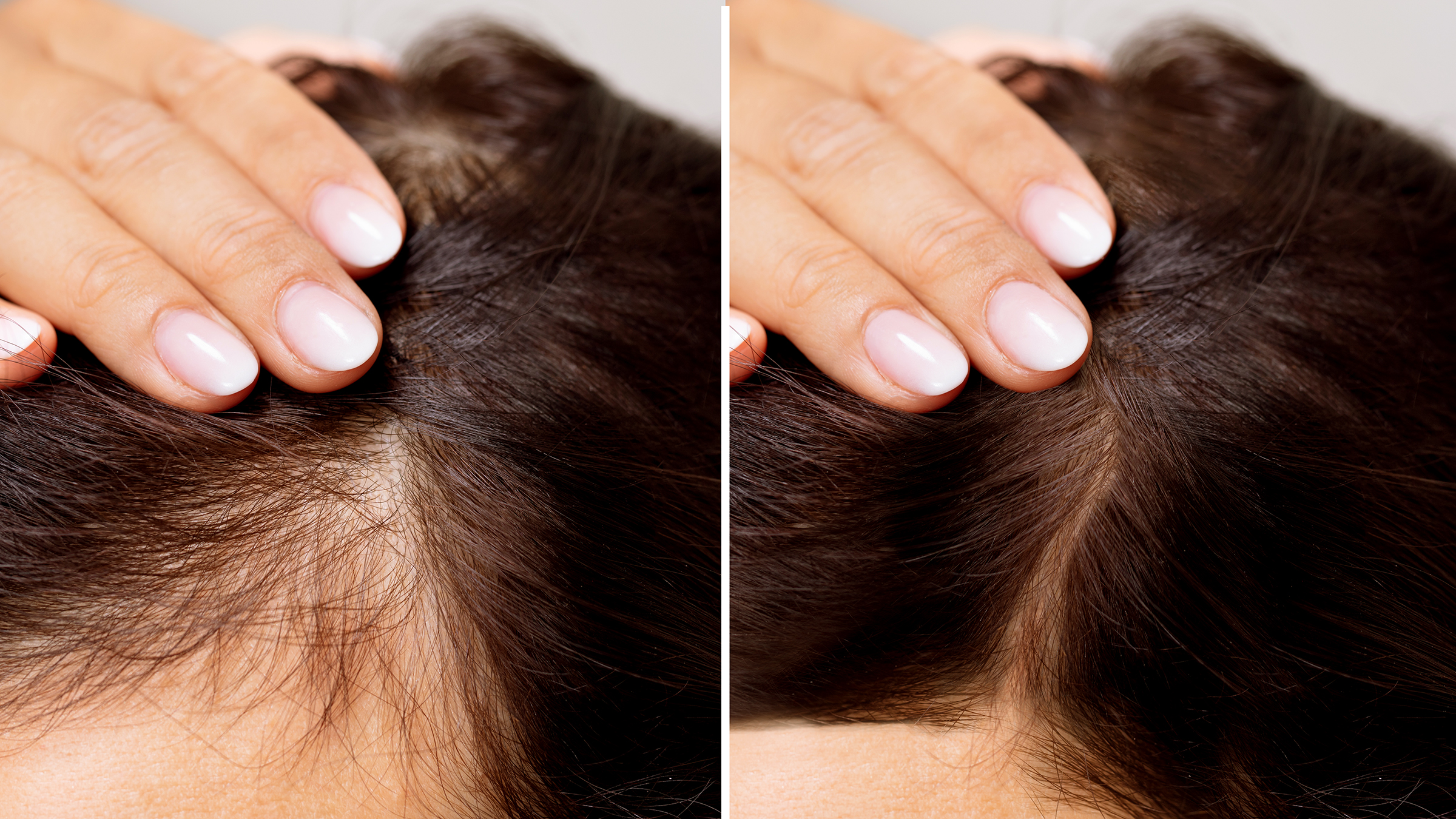
The treatment of baldness or hair loss often depends on the underlying cause and the individual's specific condition. Various options are available, ranging from medications to surgical procedures. It's important to note that the effectiveness of treatments can vary, and not all options are suitable for everyone.
Common Treatment Options for Baldness/Hair Loss:
-
Minoxidil:
- Minoxidil is a topical over-the-counter medication that is applied directly to the scalp. It is approved by the FDA for both men and women. Minoxidil is thought to increase blood flow to the hair follicles, promoting hair growth and preventing further hair loss.
-
Finasteride:
- Finasteride is an oral prescription medication that is primarily used for treating male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia). It works by inhibiting the action of the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is implicated in hair loss.
-
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT):
- LLLT devices, such as laser combs or helmets, use low-level lasers or light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth. The mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it is believed to improve cellular function.
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
- PRP therapy involves drawing a small amount of the patient's blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and then injecting the PRP into the scalp. The growth factors in PRP are thought to stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth.
-
Hair Transplantation:
- Hair transplantation involves harvesting hair follicles from areas of the scalp with healthy hair growth (donor areas) and transplanting them to areas with thinning or no hair (recipient areas). This surgical procedure is effective for certain types of hair loss, such as androgenetic alopecia.
-
Topical Corticosteroids:
- Topical corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response in cases of alopecia areata, an autoimmune condition that causes patchy hair loss.
-
Dutasteride:
- Similar to finasteride, dutasteride is an oral medication that inhibits DHT. It is sometimes prescribed off-label for treating male pattern baldness.
-
Hair Growth Shampoos and Topical Agents:
- Some shampoos and topical solutions contain active ingredients like ketoconazole or saw palmetto, which are believed to have mild DHT-blocking properties.
-
Hormone Therapy:
- For certain cases of hair loss in women related to hormonal imbalances, hormone therapy may be considered to address the underlying cause.
Considerations:
-
Consultation with a Healthcare Professional:
- Before starting any treatment for hair loss, it's important to consult with a healthcare professional or a dermatologist to determine the underlying cause and receive personalized advice on suitable treatment options.
-
Effectiveness and Expectations:
- The effectiveness of treatments varies among individuals, and results may take time. It's essential to have realistic expectations and be patient with the chosen treatment.
-
Side Effects and Risks:
- Different treatments come with potential side effects and risks. For example, finasteride may have sexual side effects in some individuals. Discuss potential side effects with your healthcare provider.
-
Combination Therapy:
- In some cases, a combination of treatments may be recommended to enhance effectiveness. For example, some individuals use both minoxidil and finasteride for a synergistic effect.
-
Lifestyle and Nutritional Factors:
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and managing stress, can contribute to overall well-being, which may impact hair health.
It's crucial to seek professional guidance to determine the most appropriate treatment based on the type and cause of hair loss. The choice of treatment should be tailored to individual needs, and the potential risks and benefits should be thoroughly discussed with a healthcare provider.